Brass Instruments
- Brass instruments [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brass_instrument] are usually made of brass which is where the name comes from although they have been made of other things like wood, tusks and shells.
- Brass instruments are long pipes which widen at the end into bell shape, they have been twisted and curved to make them easier to play!
- They produce sound by vibrating your lips against them creating a "buzzing" sound.
- The pitch and sound is mostly made my pressing on valves which open and close different parts of the pipes. An exception is the trombone which is played by sliding the pipes to lengthen and shorten the pipes.
Learn more about the Brass and other instruments for younger children [https://www.bbc.co.uk/teach/school-radio/music-ks1-instruments-together-index/zkqphbk] or watch a video about brass instruments [https://www.bbc.co.uk/teach/class-clips-video/music--science-ks2-how-brass-instruments-make-sound/zknmhbk]
Below you can find out more about the different instruments.
Trumpet
- The trumpet [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trumpet] is an ancient instrument traditionally made from horns or shells. It is one of the smaller brass instruments and plays the highest pitch with a bright vibrant sound. The trumpet is a slender brass pipe with three valves.
- You play the trumpet by holding it in a horizontal position, buzzing you lips on the mouthpiece and pressing down on the three valves in different combinations to change the pitch.
- If you stretch it out to its full length it would be 6 and 1/2 feet long!
- There are usually 2 to 4 trumpets in an orchestra and they play both the melody and the the harmony.
Cornet
- The cornet [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cornet] is a brass instrument similar to a trumpet but distinguished by its conical bore and shorter twisted shape. It also produces a more mellow tone than a trumpet.
- It is perfect for beginners and young children due to its compact size.
- The modern-day cornet is used in brass bands, concert bands and other orchestral music that requires a more mellow sound.
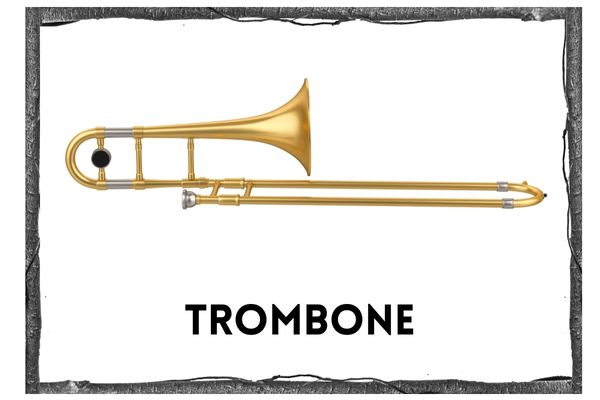
Trombone
- The trombone [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trombone] uses a slide instead of valves to change the pitch. It is made of long thin brass pipes. One pipe slides into the other so the total length of the pipe can be extended or shortened.
- You play the trombone by holding it horizontally, buzzing into the mouthpiece, and using your right hand to change pitch by pushing or pulling the slide to one of seven different positions.
- A trombone when fully stretched out straight measures about 9 feet long!
- There are usually 3 trombones in the orchestra and they play pitches in the same range as the cello and bassoon. The three trombones often play harmonies together.
Baritone
- The baritone [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Baritone_horn] is a musical instrument [https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Musical_instrument] like a tuba [https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tuba] but smaller and higher pitched. It is also known as a baritone horn.
- it is a brass instrument, and it usually is played primarily in base clef. It has a similar sound to a trombone.
- You play the baritone by holding it in a horizontal position, buzzing you lips on the mouthpiece and pressing down on the three valves in different combinations to change the pitch.
- It is a nine-foot brass tube with piston-style valves. It is narrow and smaller than a euphonium.
- The baritone is part of the tenor section of a band, and has a brighter more vibrant sound than other larger brass instruments,
Euphonium
- The euphonium [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euphonium]is a brass instrument [https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brass_instrument]. It is very similar to the baritone horn [https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Baritone_horn], but it is different because the tubes are wider and it is bigger.
- The euphonium makes low sounds, similar to the trombone [https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trombone],
- You play it by blowing into the instrument and "buzzing" with your lips and pressing valves to change the pitch
- The word euphonium means: "producing nice sounds"
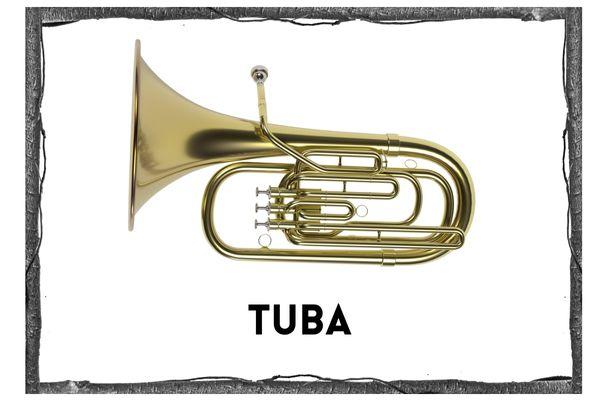
Tuba
- This is the grandfather of the brass family. The tuba [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tuba] is the largest and lowest brass instrument and has a deep rich sound.
- You play the tuba sitting down with the instrument on your lap and the bell facing up. You blow and buzz into a very large mouthpiece and use your hand to press down on the valves which changes the sound. It takes a lot of breath to make sound with the tuba!
- Like the other brasses, the tuba is a long metal tube, curved into an oblong shape, with a huge bell at the end.
- Tubas range in size from 9 to 18 feet; the longer they are, the lower they sound.
- There is generally only one tuba in an orchestra and it usually plays harmony.
Find out more about musical instruments on the BBC Bitesize website [https://gb.abrsm.org/en/exam-support/apps-and-practice-tools/]
Woodwind Instruments
- Woodwind instruments [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Woodwind_instrument] are usually played by blowing on a reed attached to a mouthpiece of an instrument (like a clarinet) or by blowing across a hole in a tube (like a flute).
- The notes are played by opening and closing the holes on the instrument.
- Many woodwind instruments are made in several parts that are fitted together.
- The instruments in this family all used to be made of wood, which gives them their name. Today, they are made of wood, metal, plastic or some combination.
- They are all basically narrow cylinders or pipes, with holes, an opening at the bottom end and a mouthpiece at the top.
- The mouthpieces for some woodwinds, including the clarinet, oboe and bassoon, use a thin piece of wood called a reed, which vibrates when you blow across it.
- Just as with the stringed instruments, the smaller woodwinds play higher pitches while the longer and larger instruments play the lower notes.
Find out more about the different woodwind instruments below.
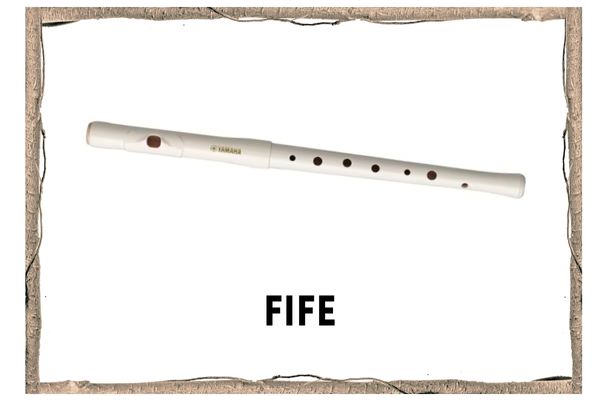
Fife
- A fife [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fife_(instrument)]is a small, high-pitched, aerophone [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aerophone], that is similar to the piccolo [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Piccolo]. It originated in medieval Europe and is often used in fife and drum corps [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fife_and_drum_corps], military units [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Military_band], and marching bands [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Marching_band].
- Fifes are made primarily of wood, but some fifes are entirely made of metal or plastic.
- It is a tube with holes, which you play by blowing across a embouchure hole and covering the 6 finger holes with both hands to change the pitch
- Fifes are most commonly used in Fife and Drum Corps, but can also be found in folk music [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Folk_music], particularly Celtic music [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Celtic_music]. Some Caribbean music [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Caribbean_music] makes use of fifes, which are usually made from bamboo [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bamboo].
Recorder

- The recorder [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Recorder_(musical_instrument)] is first documented in Europe in the Middle Ages, and continued to enjoy wide popularity in the Renaissance and Baroque periods. It was revived in the twentieth century as part of the historically informed performance movement, and became a popular amateur and educational instrument.Shakespeare mentions the recorder in Hamlet, written at the turn of the seventeenth century,
- The recorder produces sound in the manner of a whistle or an organ flue pipe. The recorder is held with both hands, covering the fingerholes or depressing the keys with the pads of the fingers: You make a sound by blowing into the head joint and covering the finger holes, in combination or partially covered, the change the pitch and sound of the instrument.
- recorders are popular in schools, as they are one of the cheapest instruments to buy in bulk They are also relatively easy to play at a basic level because sound production needs only breath, and pitch is primarily determined by fingering
- The recorder is a very social instrument and many recorder players participate in large groups.
Flute
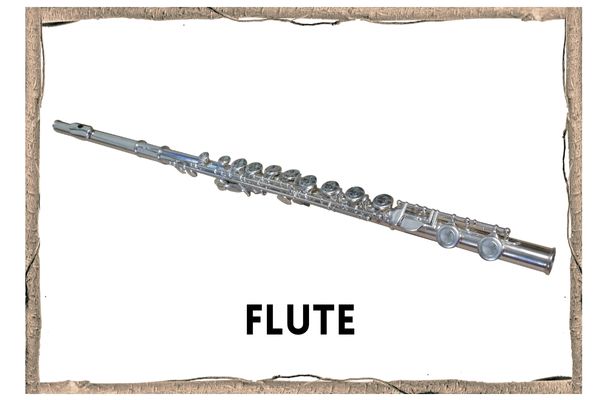
- The flute [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flute] is the oldest of all instruments that produce pitched sounds (not just rhythms),
- You play the flute by holding it sideways with both hands and blowing across a hole in the mouthpiece, much like blowing across the top of a bottle. Your fingers open and close the keys, which changes the pitch.
- It was originally made from wood, stone, clay or hollow reeds like bamboo. Modern flutes are made of silver, gold or platinum;
- there are generally 2 to 4 flutes in an orchestra.
Clarinet

- The clarinet [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Clarinet] could easily be mistaken for an oboe, except for the mouthpiece, which uses a single reed.
- You play the clarinet as you do an oboe, by holding it upright, blowing through the reed, and using your hands to change the pitches by opening and closing the keys with your fingers.
- Clarinets come in a number of different sizes, and the standard B-flat clarinet is just over 2 feet long. Some musical works require the clarinetist to play several types of clarinet in the same piece.
- There are 2 to 4 clarinets in the orchestra play both melodies and harmonies, and they have a dark rich sound in their lower notes, while the upper part of the clarinet's range is bright and resonant.
Saxophone

- The saxophone [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Saxophone] is an instrument with a tone somewhere between a brass instrument and a woodwind with a smooth bright sound.
- The sax is a must in all types of music from jazz, to classical and pop,
- It is made up of brass and it is played with a single-reed mouthpiece. It has holes in it which player closes using a system of key mechanisms.
Oboe
 The oboe [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oboe] is a 2 foot long black cylinder with metal keys covering its holes, uses a double reed, which vibrates when you blow through it. T
The oboe [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oboe] is a 2 foot long black cylinder with metal keys covering its holes, uses a double reed, which vibrates when you blow through it. T
- To play it, you hold the oboe upright, blow through the double reed in your mouth, and use both hands to press down on the keys to open and close the holes and change the pitch.
- There are usually 2 to 4 oboes in an orchestra and they produce a wide range of pitches, from haunting sounds to warm, velvety smooth notes, which make the sound of the oboe very memorable.
- In addition to playing in the orchestra, the first oboist is also responsible for tuning the orchestra before each concert. Listen for the special note "A" that the oboe plays before the music begins.
Find out more about musical instruments on the BBC Bitesize website [https://gb.abrsm.org/en/exam-support/apps-and-practice-tools/]
String Instruments
- String Instruments [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/String_instrument] have strings that vibrate to make sound.
- They can be played, with a bow (like a violin), struck with hammers (like a piano), or plucked with fingers (like a guitar)
- The bodies of the string instruments, which are hollow inside to allow sound to vibrate within them, are made of different kinds of wood,
- The part of the instrument that makes the sound is the strings, which are made of nylon, steel or sometimes gut.
- The handle of the bow is made of wood and the strings of the bow are actually horsehair from horses' tails!
- The strings are played most often by drawing a bow across them.
- Sometimes the musicians will use their fingers to pluck the strings, and occasionally they will turn the bow upside down and play the strings with the wooden handle.
- They used to be known as chordophones.
Find out more about string instruments below
Upper Strings
Violin

- The violin [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Violin] is the baby of the string family, and like a baby, makes the highest sound.
- You play the violin by resting it between your chin and left shoulder. Your left hand holds the neck of the violin and presses down on the strings to change the pitch, while your right hand moves the bow or plucks the strings.
- There are more violins in the orchestra than any other instrument (there can be up to 30!) and they are divided into two groups: first and second. First violins often play the melody, while second violins alternate between melody and harmony.
- A typical-sized violin is around 24 inches (two feet) long, with a slightly longer bow.
Viola

- The viola [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Viola] is the older sister or brother of the violin. It is slightly larger, just over two feet long, and has thicker strings, which produce a richer, warmer sound than the violin.
- You play the viola the same way as you do the violin, by resting it between your chin and shoulder. Your left hand holds the neck of the viola and presses down on the strings to change the pitch, while your right hand moves the bow or plucks the strings.
- There are usually 10 to 14 violas in an orchestra and they almost always play the harmony.
Cello

- The cello [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cello] looks like the violin and viola but is much larger (around 4 feet long), and has thicker strings than either the violin or viola.
- Since the cello is too large to put under your chin, you play it sitting down with the body of the cello between your knees, and the neck on your left shoulder. The body of the cello rests on the ground and is supported by a metal peg. You play the cello in a similar manner to the violin and viola, using your left hand to press down on the strings, and your right hand to move the bow or pluck the strings.
- Of all the string instruments, the cello sounds most like a human voice, and it can make a wide variety of tones, from warm low pitches to bright higher notes.
- There are usually 8 to 12 cellos in an orchestra and they play both harmony and melody.
Double Bass

- This is the grandfather of the string family. At over 6 feet long, the double bass [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Double_bass]is the biggest member of the string family, with the longest strings, which allow it to play very low notes.
- They are so big that you have to stand up or sit on a very tall stool to play them, and it helps if you have long arms and big hands. Like the cello, the body of the double bass stands on the ground, supported by a metal peg, and the neck rests on your left shoulder. You produce sound just like on a cello, using the left hand to change pitch and the right to move the bow or pluck the string.
- The 6 to 8 double basses of the orchestra are almost always playing the harmony.
Lower Strings
Ukulele

- The ukulele [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ukulele] also called a uke, is a member of the lute family of instruments of Portuguese origin and popularized in Hawaii. It generally employs four nylon strings
- It is usually played with the bare thumb and/or fingertips, or a felt pick
- The ukulele is generally made of wood, though variants have been composed partially or entirely of plastic or other materials. More expensive ukuleles are made of solid hardwoods such as mahogany. The traditionally preferred wood for ukuleles is a type of acacia endemic to Hawaii, called koa.
- The tone and volume of the instrument vary with size and construction. Ukuleles commonly come in four sizes: soprano, concert, tenor, and baritone.
- In the Hawaiian language the word ukulele roughly translates as "jumping flea",[9] perhaps because of the movement of the player's fingers.
- British singer and comedian George Formby was a ukulele player
Acoustic Guitar

- The guitar [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Guitar] is one of the oldest and most basic instruments in the music world
- It produces sound through the vibration of strings.
- The sound is produced by plucking with the fingers or with a pick on the string. The string vibrates at a certain frequency and also creates many harmonics.
- It is one of the famous musical instruments, although it isn't included in an classical orchestra. Guitars are one of the major features of modern music.
Electric Guitar

- An electric guitar [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electric_guitar] is a guitar [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Guitar] that requires external amplification in order to be heard at typical performance volumes, unlike a standard acoustic guitar. It uses one or more pickups to convert the vibration of its strings into electrical signals, which ultimately are reproduced as sound by loudspeakers.
- You play it the same as an acoustic guitar by pressing and holding strings down with your left hand. and then striking the strings with your right hand to creates music
- It was invented in 1932, the electric guitar was adopted by jazz guitar players, who wanted to play single-note guitar solos in large big band ensembles.
- In rock, the electric guitar is often used in two roles: as a rhythm guitar, which plays the chord sequences or progressions, and riffs, and sets the beat (as part of a rhythm section); and as a lead guitar, which provides instrumental melody lines, melodic instrumental fill passages, and solos
Find out more about musical instruments on the BBC Bitesize website [https://gb.abrsm.org/en/exam-support/apps-and-practice-tools/]
Percussion
- Percussion instruments [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Percussion_instrument] are hit, scraped or shaken to create a sound with players often using their hands or sticks to hit an instrument.
- There are many types of percussion including drums, cymbals, xylophones.
- Pianos are sometimes considered to be percussion because they are similar to a xylophone.
Find out more about percussion instruments here or click on the pictures to find out more about the different percussion instruments.
Piano
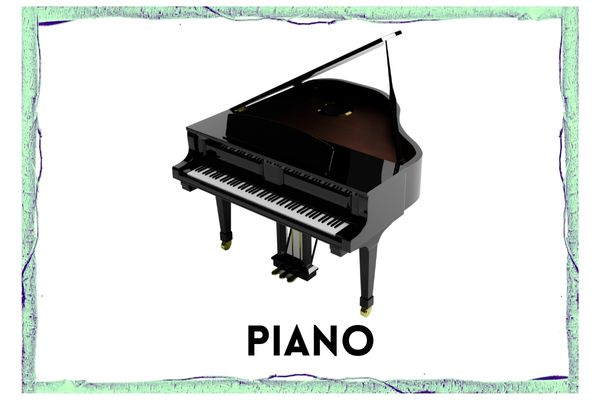

- The piano [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Piano]is a keyboard instrument [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Keyboard_instrument] with strings struck by wooden hammers coated with a softer material (modern hammers are covered with dense wool felt; some early pianos used leather).
- It is played using its keyboard, which is a row of keys (small levers) touched by the performer with the fingers and thumbs of both hands, causing the hammers to strike the strings.
- It was invented in Italy by Bartolomeo Cristofori around the year 1700.
- The English word piano is a shortened form of the Italian pianoforte which means soft and loud
- Most modern pianos have a row of 88 black and white keys: 52 white keys for the notes of the C major scale (C, D, E, F, G, A and B) and 36 shorter black keys raised above the white keys and set further back, for sharps and flats.
- The piano is a crucial instrument in Western classical music, jazz, blues, rock, folk music, and many other Western musical genres. Pianos are used in soloing or melodic roles and as accompaniment instruments
- pianos can be played alone, with a voice or other instrument, in small groups (bands and chamber music ensembles) and large ensembles (big band or orchestra).
- Bandleaders and choir conductors often learn the piano, as it is an excellent instrument for learning new pieces and songs to lead in performance and pianos are used to help teach music theory, music history and music appreciation classes.
Keyboard

- An electronic keyboard [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electronic_keyboard], portable keyboard, or digital keyboard is an electronic musical instrument, an electronic version of a keyboard instrument.[1]
- Electronic keyboards include synthesizers, digital pianos, stage pianos, electronic organs and digital audio workstations. In technical terms, an electronic keyboard is a synthesizer with a low-wattage power amplifier and small loudspeakers.
- They are played by pressing the white and black piano-style keys which when pressed connect the switches, which trigger the electronic circuits to generate sound.
- Electronic keyboards are usually designed for home users, beginners and other non-professional users. They typically have unweighted keys.and are more affordable and practical than a piano.
Drums

- A drum kit [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Drum_kit](also called a drum set, trap set, or simply drums) is a collection of drums, cymbals, and sometimes other percussion instruments set up to be played by one person.[1]
- The player (drummer) typically holds a pair of matching drumsticks, one in each hand, and uses their feet to operate a foot-controlled hi-hat and bass drum pedal.
- The drum kit is a part of the standard rhythm section and is used in many types of popular and traditional music styles, ranging from rock and pop to blues and jazz
Find out more about musical instruments on the BBC Bitesize website [https://gb.abrsm.org/en/exam-support/apps-and-practice-tools/]








